Tel: +86 17310763143
E-mail: sales@nmgymjx.com
Website: www.nmgymjx.com
Address:The intersection of G242 and 311 roads, Langshan town, Linhe district, Inner Mongolia, China.
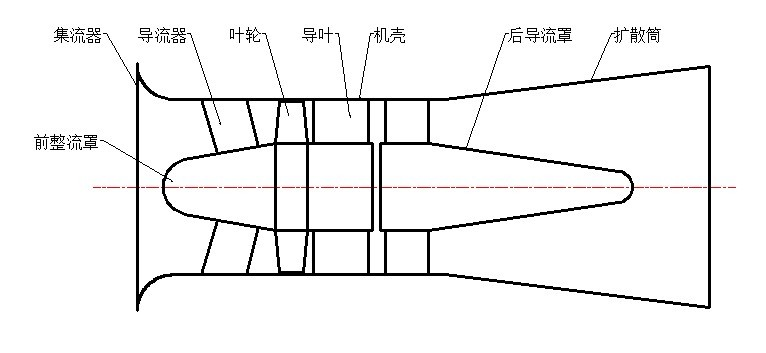
The axial flow fan has gradually replaced the centrifugal fan with the advantages of large flow, small starting torque and strong adaptability to the change of the air duct system. The axial flow fan has two adjustment modes: the moving blade and the stationary blade. ·
The adjustable axial flow fan of the moving blade changes the working condition by changing the angle of the working blade. There is no interception loss, the efficiency is high, and the instability phenomenon can be avoided under the small flow condition, but the structure is complicated, and the stability of the adjusting device is The reliability requirements are high, the manufacturing precision is also high, and the fault is easy to occur, so it is generally only used for the blower and the primary fan.
The fixed-leaf adjustable axial flow fan changes the working condition by changing the flow area and the inlet airflow direction, and has a cut-off loss, but its structure is simple, and the failure rate of the adjustment mechanism is very low, so it is generally used for an induced draft fan with a poor working environment.
With the wide application of axial fans, the vibration problems corresponding to their structural characteristics are gradually exposed. These problems are not present or uncommon on centrifugal fans. This paper summarizes the abnormal vibration faults of various axial flow fans and summarizes some of the characteristic vibrations and their causes.
First, the moving blade adjustment structure causes vibration
The adjustable blade axial flow fan changes the operating condition of the fan by adjusting the opening degree of the blade online, which mainly depends on the hydraulic adjustment control mechanism in the hub, and the adjustment of each blade angle involves a series of adjustment components, thus The installation and fitting of components and the deformation and wear requirements of the components themselves are high. The structure of the hydraulic blade adjustment system is shown in Figure 1. The influence of the blade adjustment structure on the vibration is mainly divided into three aspects: the partial blade opening degree of the single-stage impeller is not synchronized, the blade opening degree of the two-stage impeller is not synchronized, and the adjustment component itself is eccentric.
1. Single-stage impeller part blade opening is not synchronized
The unsynchronized opening degree of the blade of the single-stage impeller is mainly caused by the wear of the slider, the loosening of the adjusting rod and the crank, the poor rotation of the petiole guide bearing and the thrust bearing. These components are transmission matching components between the hydraulic cylinder and the moving blades, which may cause some of the fan blades to be out of position, and the fan blade weight and installation radius are large, and some fan blade opening degrees are inconsistent, resulting in serious imbalance of quality. This causes the fan to vibrate significantly at high speeds.
2. Two-stage impeller blade opening is not synchronized
For the two-stage moving blade adjustable axial flow fan, there is also a problem that the two-stage impeller blade opening degree is not synchronized. The main reason is the wear of the copper sleeve of the hydraulic actuator or the wear deformation of the two-stage thrust cross-link. The connecting rod is mainly used to synchronize the axial displacement between the first and second thrust plates, and the wear deformation of the connecting rod causes the displacement between the two stages of the thrust plates to be out of synchronization, thereby causing the two-stage moving blade opening degree to be unsynchronized. The wear, partial cracking, deformation and the increase of the central shaft clearance of the copper sleeve of the hydraulic cylinder will result in the overall adjustment of the opening degree of the two-stage bucket not being in place, so that the opening degree of the two-stage bucket is inconsistent. Since all blade opening degrees of a single impeller are synchronized, it does not significantly affect the dynamic balance of the rotor. Therefore, the power frequency ratio in the vibration fault spectrum is generally relatively small, mainly due to the large blade passing frequency. In the case of severe looseness, power frequency higher harmonic components will also appear. The amplitude generally has a large value under a certain load (the blade opening degree), and the amplitude fluctuates, in which the power frequency and the blade passing frequency both fluctuate, while the amplitude is relatively small under other loads or without load. .
3. Adjusting component eccentricity
The eccentricity of the adjusting component mainly refers to the eccentricity and looseness of the adjusting component with large mass. Due to the large mass, when the center of rotation and the center of the rotor are skewed, a large mass imbalance will occur, and the eccentricity caused by loosening will occur. There will also be a quality imbalance. For the movable blade adjustable axial flow fan, it mainly refers to the installation eccentricity and looseness of the hydraulic cylinder. If only the hydraulic cylinder is installed with eccentricity and the tightening force is sufficient, it will only lead to a change in the mass distribution. The fan rotor will have a simple mass imbalance fault. The fault spectrum is mainly a stable power frequency component. The vibration values are relatively stable and will not change with load conditions. If it is loose due to insufficient tightening force when the hydraulic cylinder is installed, an unstable mass imbalance will occur, and the machine will start again after each stop. The position of the hydraulic cylinder will change due to the change of centrifugal force, causing each time to start. The vibration data are inconsistent, the vibration is mainly based on the power frequency, and the vibration is relatively stable when the rotation speed is constant. For such faults, the vibration is very stable after a single constant speed, which is easily confused with the original mass imbalance, resulting in unnecessary repeated dynamic balance.
Second, the airflow pulsation causes vibration
Airflow pulsation is a ubiquitous product of gas flow separation and vortex development. For the axial flow fan, in addition to the fluid pulsation caused by the unreasonable design of the flow passage structure such as the inlet and outlet flow passages and baffles in the original design and the later modification, the reasons for the fluid pulsation in the axial flow fan are as follows:
The stability of the blade opening of the adjustable axial flow fan is large. The change of the opening degree of the static blade under low load easily causes the working point of the fan to fall into the unstable operation area, causing fluid pulsation and even surge, causing strong vibration.
Due to welding stiffness, local stress, corrosion or foreign matter entering, the rotor blades and vanes of the fan are seriously worn or even partially detached, causing fluid pulsation.
Due to the abnormal flow passage baffle of the fan inlet and the blockage of foreign matter, the system resistance increases and the flow rate is insufficient, causing fluid pulsation, stall and even surge.
The actual test data on the site shows that the vibration phenomena and characteristics of the fan caused by the above several fluid pulsations are similar, including the following:
The pulsation of the air flow causes vibrations of the fan casing, the inlet and outlet pipes and the casing foundation, and has little influence on the mechanical vibration of the bearing and the rotor. The starting frequency is mainly the low frequency component which is independent of the main frequency of the rotor.
When the moving blade or vane wears and ruptures to generate airflow pulsation, the airflow pulsation will be coupled with the mechanical vibration. At this time, the blade pulsation fault frequency will have a large blade passing frequency and its harmonics, and the bearing and the rotor will also The frequency of failure occurred.
In addition to causing the vibration of the fan, the airflow pulsation will also cause the fan current, flow instability, and even large fluctuations. As a result, the two fans operating in parallel have a large current difference under the same air volume, and there is obvious airflow noise at the site.
Third, the support dynamic stiffness is weak and local resonance causes vibration
Compared with the centrifugal fan, the large-capacity axial flow fan has larger self-weight and outer dimensions, and more support connecting members. The vibration problem caused by weak design, loose connection and local resonance is more difficult and difficult to distinguish. .
1. Design support is weak in dynamic stiffness
Large-capacity axial flow fans increase in weight and size, while support materials tend to be weak. The fan adopts 3 cement seat support methods, that is, the air intake box leg, the lower casing leg and the diffusion tube leg are respectively supported on three cement blocks, each cement base has a high height, insufficient cross-sectional area, and lateral direction. The rigidity is poor, which is easy to cause large lateral vibration of the fan. Especially when the fan load is high, the force transmitted by the fan rotor to the base increases, and the amplitude is larger.
In the absence of an abnormal excitation source, the vibration caused by the weak stiffness of the design support structure is mainly based on the power frequency. The foundation of the support structure, the legs and the shell are relatively close in amplitude, and are uniformly reduced from top to bottom, but the overall vibration of the support structure is large, mainly in the horizontal direction, while the vertical and axial vibrations are generally small. Generally, by dynamic balancing or reinforcing the support foundation, the rotor exciting force can be reduced, thereby reducing the vibration level of the fan.
2. Loose connection
The lower part of the axial flow fan housing is connected to the cement base through the legs, and is connected to the air inlet box and the diffusion tube by a ring of bolts on the left and right sides, and the upper and lower half cylinders are connected by two rows of bolts, and the bearing seat is fixed in the lower half of the housing. on. Due to the large number of connecting parts of the axial flow fan housing, the tension is insufficient and the connection is loose during long-term operation, and the vibration caused by the loose connection of some axial flow fans is very large, especially the resonance frequency and working speed of the housing. When they are close, the loose connection often leads to the inherent spectral shift of the casing, resonance occurs, and the vibration is further amplified. If the connecting bolts of the fan casing and the left and right air duct shells are partially loosened, the amplitude of the casing can be enlarged by more than one time. When the casing loosens to resonate, even one order of magnitude vibration difference may occur, and some large-capacity units may The lower support of the axial flow fan adopts a spring foundation. After a long time of operation, uneven foundation settlement occurs, which also causes the support dynamic stiffness to be obviously insufficient, resulting in obvious vibration.
The vibration caused by the weak connection of the fan causes the vibration of the support to be weak, and is generally eliminated by field fastening. Such vibrations are mainly based on power frequency, and have certain fluctuations with load changes. The differential vibration of loose contact surfaces is obvious. Generally, the bolts of each joint surface should be tightened first. For those with sliding legs, the legs are fastened and the legs are tested. Then test each. The difference in vibration of the contact surface and the vibration before and after the fastening to check for loose connection problems.
3. Local resonance
Due to the structural characteristics of the axial flow fan, the natural frequency near the rotational frequency and the blade passing frequency is large, and local resonance is easily generated. For example, each leg of the fan, the upper and lower housings, the support plate, the blade, etc. have one to several natural frequencies, and some of the blade passing frequencies are very close to the common fault frequency of the fan, which easily causes local resonance.
For such vibration problems, it is difficult to greatly change the natural frequency of each structure in the field. Generally, after tightening the connection faces to eliminate the resonance caused by the loose connection, the vibration level is reduced by reducing the excitation force. If the dynamic balance is used to reduce the power frequency excitation force, or the blade opening degree is consistent, the blade uneven wear condition is checked, and the excitation force of the blade passing frequency is reduced.
Fourth, vibration troubleshooting recommendations
1. When dealing with abnormal vibration of large-capacity axial flow fans, in addition to the conventional fault frequency analysis, the characteristics of vibration changes should also be analyzed, such as changes in vibration with time, load, opening, ambient temperature, etc. Constant speed and vibration under load, test of differential vibration and elastic bolt vibration of the connected parts on site.
2. When the difference of the vibration law of the secondary dynamic balance is large, the balance block added in the previous stage should be removed, and the coincidence of the vibration after the start of the machine 2 times should be tested to find out the cause of the vibration change.
There are many reasons for the failure of the hydraulic adjustment structure of the adjustable axial flow fan. When it is found that the vibration is highly correlated with the blade opening degree, and there is obvious blade passage frequency or power frequency harmonic, the hydraulic adjustment structure should be investigated for looseness, wear and other defects. .
Reprint statement:
The article is reproduced on the Internet for the purpose of transmitting more information and does not imply endorsement of its views or verification of the authenticity of its content. If the reprinted works infringe the author's right to authorize, or have other damages such

De-impurity

Delivery of the wind for raw material

Dmс-160 type pulsed jet cloth filter

Grading screen

Polisher
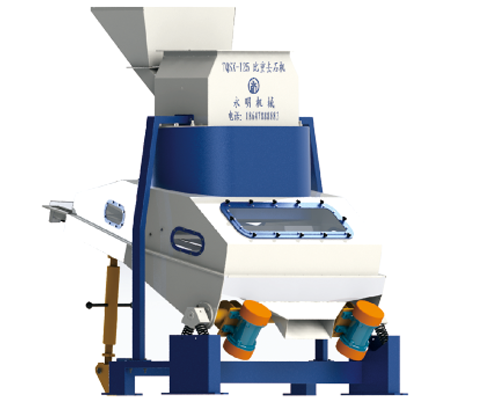

De-stoner
Unbroken elevator
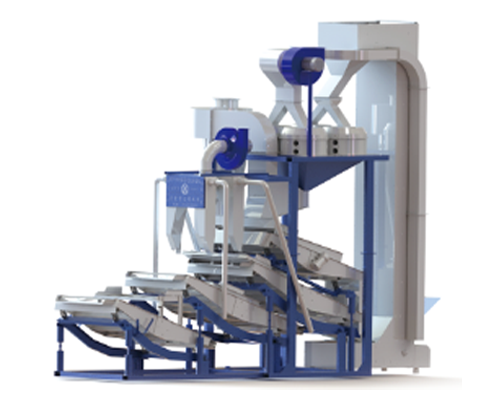

KTF4-3000 Sunflower seed hulling & separating machine
Ident cylinder sunflower seed cleaning machine
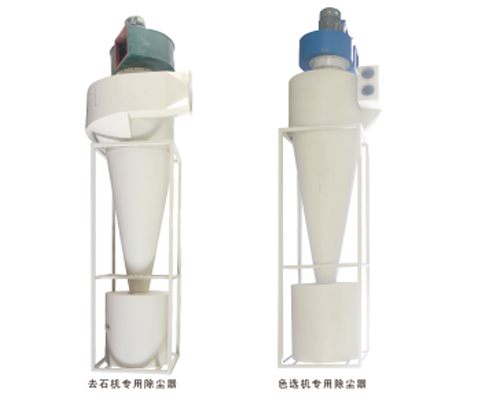

Product introduction of cyclone dust separator
Vertical hoist
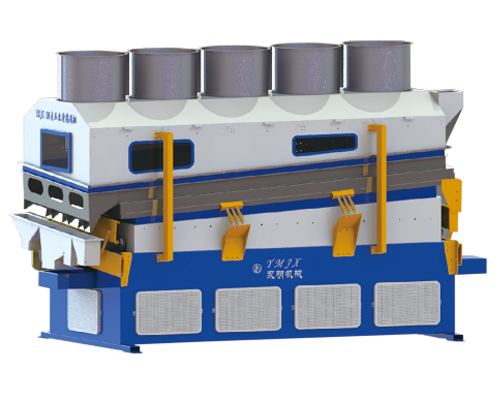

Gravity separator
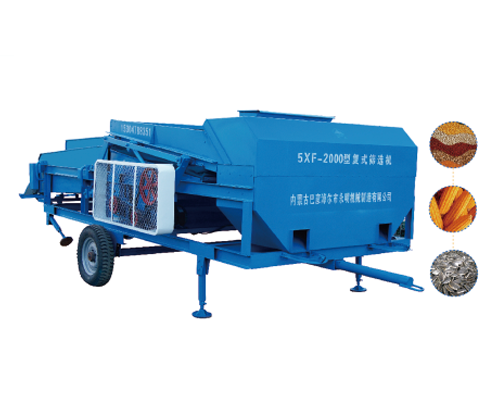

5XF-2000 type compound screening machine
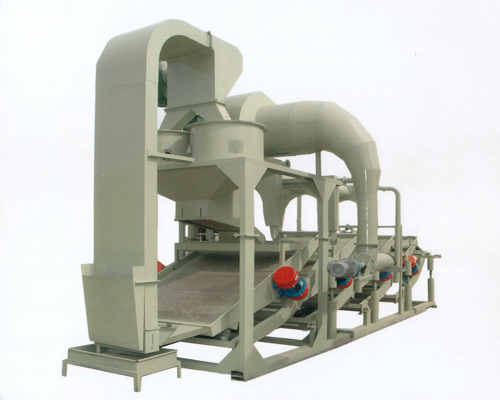

KTF3-1200 Sunflower seed hulling & separating machine
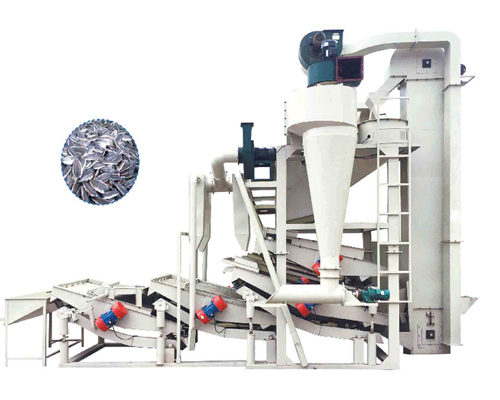

KTF4-2800型葵花脱壳分选机