Tel: +86 17310763143
E-mail: sales@nmgymjx.com
Website: www.nmgymjx.com
Address:The intersection of G242 and 311 roads, Langshan town, Linhe district, Inner Mongolia, China.
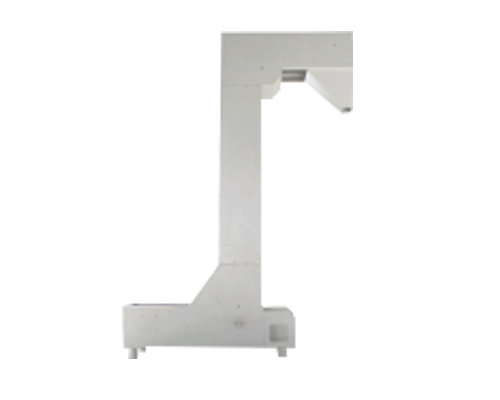
This article introduces some problems that may occur in the Z-type bucket non-crushing hoist and provides possible solutions. Bucket type non-crushing hoist lifts bulk materials from one height to another. They are used in powders, granules, granules, flake products and bulk materials. When they are properly designed for the task, they work well and are used as designed. The following editors take a closer look at them.
The bucket is bolted to the belt and is driven by a pulley. The frame and shell surround the belt, bucket and product. The bucket lifts the material fed into the elevator base or luggage. At the top, throw it out of the exit chute. Adjustable screws move one of the pulleys to provide belt tensioning and tracking. The top and bottom inspection doors allow you to see the belt while making tracking adjustments.
1.Drive pulley
The drive pulley can be a top pulley or a bottom pulley. The motor and gearbox are driven by top pulleys, free of product spillage and dust. The belt tension need only be sufficient to provide sufficient friction between the belt and the pulley to lift the material.
Belt tracking and maintenance require an access platform for top drive of the elevator. With the bottom pulley drive, maintenance is easy, but the belt tension is doubled to provide the same drive friction. This increases the load on all moving parts. If the bottom drive wheel is coated with a product coating or the belt is stretched, the belt will slip. There are fewer operational problems with the top pulley drive.
2.The importance of cleanliness
When bucket elevators are used in a variety of products, they require quick cleaning by the operator. The flange and bolt access doors are well sealed, but disassembly is slow and the threads may become dusty. The bottom pulley should be self-cleaning and should not allow product to accumulate between the belt and the pulley. One method is to create a grizzly design using a round stick. Sticking rubber to the drive wheels increases driving friction. The rubber joint is cut at a 45-degree angle from the pulley shaft so that the joint gradually enters the friction area of the pulley.
3.Belt speed
Belt speed requires the material to be discharged from the bucket and into the discharge chute. The speed is too slow and the material slides from the tipped bucket over the top pulley and back to the bottom of the elevator. The speed was too fast, the material was thrown too fast, hit the top of the elevator, and then fell back to the bottom. This formula can be used to determine the correct belt speed and material throw.
4.Shaft seal
The pulley bearing should be installed on the bracket outside the elevator cabinet as far as possible to prevent the shaft seal from leaking. Shaft seals should be designed to prevent leakage. Refer to the article on protecting bearings in dusty environments.
5.Feeding trough
The product is fed into the elevator hood by passing the material through the chute under gravity or by a forced method (such as a power feeding screw). The angle of the feed slot and its cross section need to be large enough to prevent product hanging or accumulation. Unblocked access is essential. Similarly, the angle, size, and design of the bins need to allow the product to flow freely.
6.boost
Pressurization usually occurs inside the elevator cabinet, as the blades drag air from the top to the bottom. When the feed speed into the elevator shroud is lower than the bucket's disassembly speed, the airflow will pass through the filling section and flow upward with the full bucket. The dust rises inside the elevator, and the internal air pressure forces the dust out through the openings and seals. This problem is more serious for powdery or dusty products.
7.Dealing with dust
If reducing the amount of dust is important, you should suffocate the boot cover and do not drop the elevator into the dirt. Increasing the feed rate of the boots slightly above the bucket removal speed can cause blockages. For this paper feeding device, it is also necessary to install a back-off detection device to stop the paper feeding periodically until the guide is cleared. Another method that has been successfully used for powder products is to feed the product from below the elevator. In this way, the product filled with the protective cover moves with the bucket, and both the product and the bucket isolate the bottom of the protective cover from the airflow.
8. Mud detection
It is important to quickly detect and stop the feed of the bucket elevator into the mud. When this setting is ignored, the belt will stop, but the drive will continue to run. If not detected, the rubber on the drive wheels will fall and the belt will wear out. To detect jams, a proximity detector is installed to confirm that the non-drive shaft is rotating.
Today's content is introduced here for the time being. We will regularly release more related content. If you want to know more, please pay attention to the official website of Yongming Machinery. Thank you for your long-term support!

Reprinted statement:
This article is reproduced on the Internet for the purpose of conveying more information, and does not mean to endorse its views or confirm the authenticity of its content. If the reprinted work infringes the author's authorship, or has other damages such as copyright, portrait rights, intellectual property rights, etc., this is not intentional by this website, and will be corrected immediately after receiving the relevant right holder's notification.

De-impurity
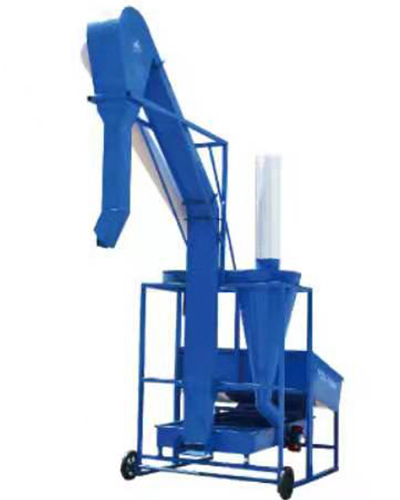

Delivery of the wind for raw material

Dmс-160 type pulsed jet cloth filter
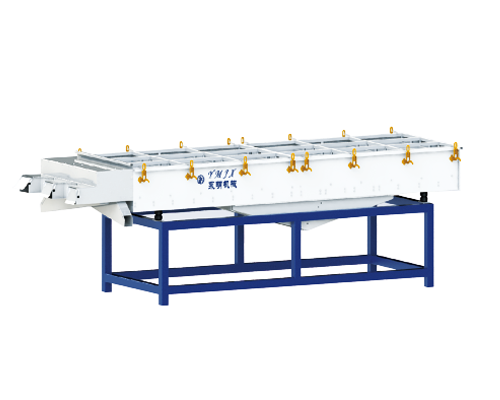

Grading screen

Polisher
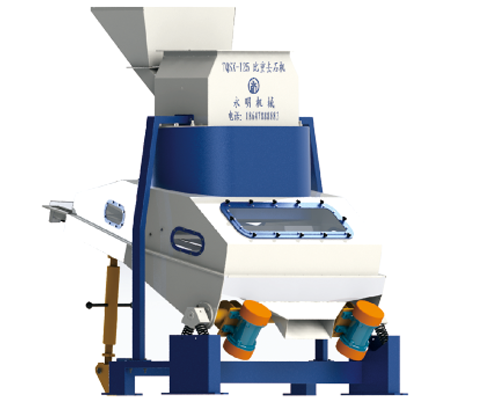

De-stoner
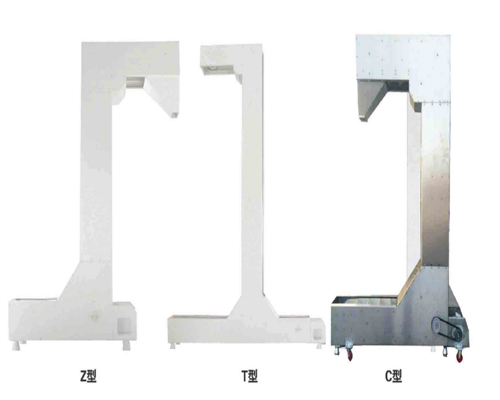
Unbroken elevator
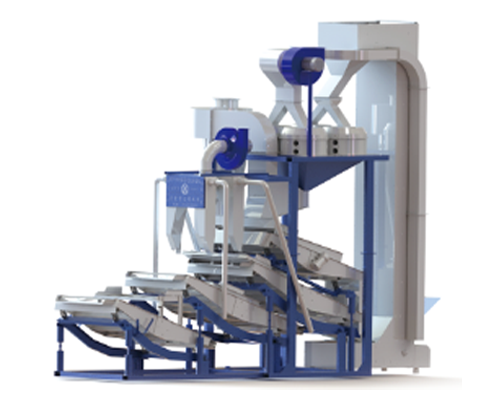

KTF4-3000 Sunflower seed hulling & separating machine
Ident cylinder sunflower seed cleaning machine
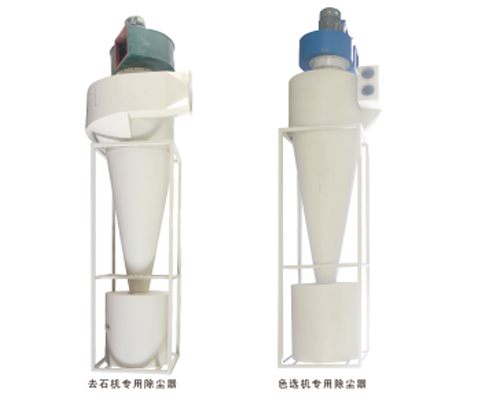

Product introduction of cyclone dust separator
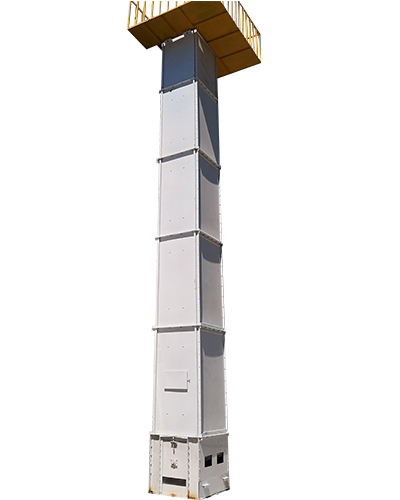
Vertical hoist

Gravity separator

5XF-2000 type compound screening machine

KTF3-1200 Sunflower seed hulling & separating machine

KTF4-2800型葵花脱壳分选机